PROJECT Organization and Component
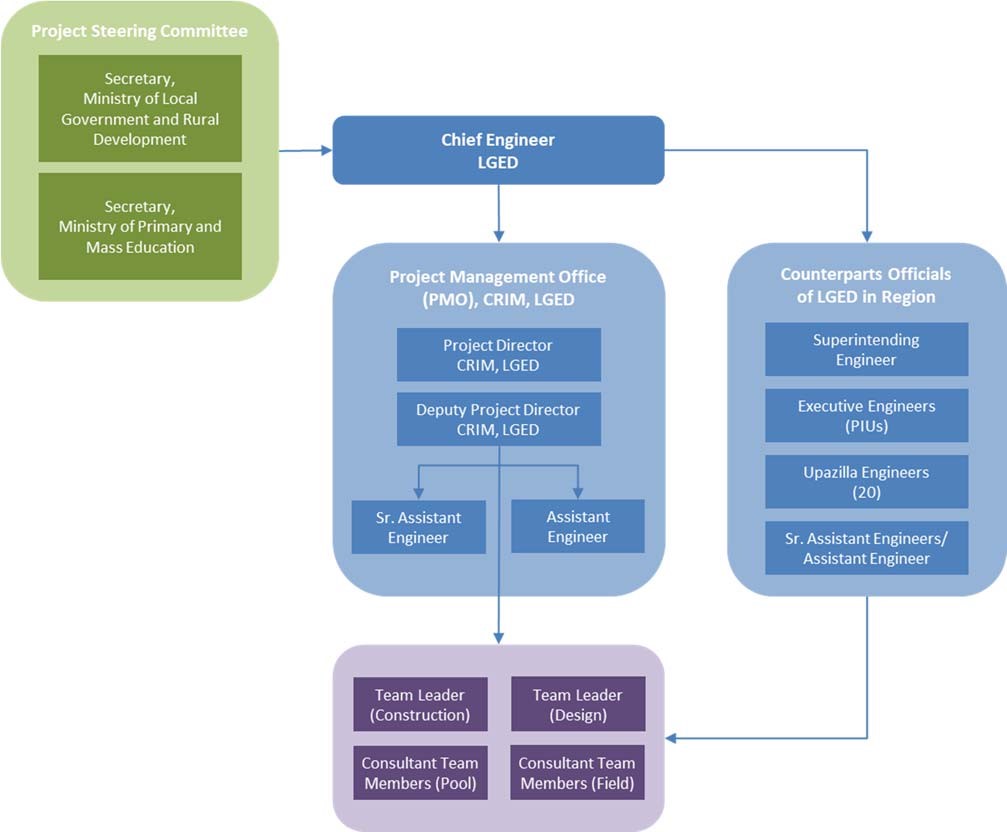
The CRIM Project is targeting three of the country’s most vulnerable and poor coastal districts of Bangladesh: Satkhira, Barguna, and Bhola. It integrates climate change adaption systematically into decision-making procedures for infrastructure planning, supervision and maintenance at LGED. The project has an overall volume of 80 million USD. The GCF provides a grant of 40 million USD. Through KfW, the German Financial Cooperation provides parallel co-financing of about 12 million EUR (equivalent to 15 million USD).
The CRIM Project is split into four Components. Within Component 1 “Institutional Development”, the project will establish within the LGED the “Climate Resilient Local Infrastructure Centre (“CReLIC”)”, a national centre of excellence to gather, develop, and share climate resilience infrastructure knowledge. The CReLIC shall be established as a permanent unit within LGED and serve as a think tank and knowledge hub to mainstream climate resilience into all LGED activities. The centre will trigger a step-wise institutional learning process all over the LGED infrastructure portfolio and pilot innovations directly in LGED operations through investments in rural and urban pilot infrastructures in three of the country’s most vulnerable and poor coastal districts: Bhola, Barguna and Satkhira.
Within Component 2 “Pilot Climate Resilient Rural Infrastructure”. the CRIM Project shall build 45 new multipurpose cyclone shelters with innovative design in climate change aspects and rehabilitate 20 existing shelters to a climate-proof standard in the three project districts (Districts Bhola, Barguna and Satkhira) in parallel. The newly built shelters shall follow an innovative state-of-the-art multi-purpose design and will be used as schools throughout the year. The CRIM Project will also improve 82 km of critical access roads to these rural shelters to ensure access during extreme weather and to enhance the adaptive capacities of local communities.
Under Component 3 “Pilot climate-resilient urban infrastructure measures in the City of Satkhira” (Satkhira Purashava/Municipality), the CRIM Project foresees improvements to drainage, flood protection, sanitation, water supply, and transport infrastructure, with priority given to the most vulnerable such as the inhabitants of city slums.
Table 1 below gives an illustrative overview of the various CRIM Project components and the respective financing sources. The Services procured under this tender shall be delivered in relation to the infrastructure measures supported under Component 2 and 3. Under Component 3, project-related capacity building and training is also expected. The Services are part of the overall project management, which is elaborated in Component 4 and which also includes the institutional development consulting (subject of a separate consultancy)
| CRIM Project Components |
Measures foreseen and financing sources |
| Component-1: Institutional Development |
Establish the “Climate Resilient Local Infrastructure Centre (CReLIC). Green Climate Fund (GCF) and GoB |
| Component 2 :Pilot Climate Resilient Rural Infrastructure |
Construction and/or rehabilitation of Multipurpose Cyclone Shelters and roads as pilot rural infrastructure for mainstreaming through CReLIC in the districts of Satkhira, Barguna and Bhola. Green Climate Fund (GCF) and GoB |
| Component 3: Pilot Climate Resilient Urban Infrastructure |
Building of high-priority climate resilient urban infrastructure in Satkhira, city drainage, flood protection, water supply, sanitation, and transport. Financing source: KfW and GoB |
| Component-4: Project Management |
Institutional Development and Design, Management and Supervision Support (DMS) for Component 2 and 3. Financing sources: Green Climate Fund (GCF) and GoB ,KfW (BMZ) and GoB for the Design, Management and Supervision (DMS) support for component 3. |





